When Is A Dog Considered An Adult

If you’re pondering “when is a dog considered an adult,” cherish your new puppy’s cuddly phase because they’ll soon grow big enough to need a new collar!
Puppies mature surprisingly quickly, but at what point do they cross into adulthood?
Read on to find out when a pup is no longer just a puppy, and to gain insight into the various growth stages your canine companion will experience.
When does a dog transition from puppy to adult?
Like many dog lovers, you might always see your furry friend as a puppy, even when they’re fully grown. Typically, a dog is considered an adult between 1 and 2 years old, once they’ve stopped growing and reached their final size.
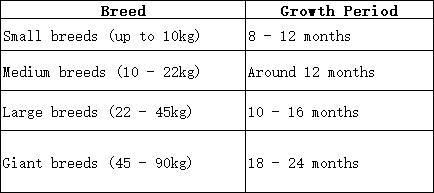
Smaller breeds often reach full size quicker, usually by 8 – 12 months. In contrast, larger and giant breeds take significantly longer to reach full maturity.
Regarding diet, how long should a dog eat puppy food?
Puppies, with their boundless energy, require extra calories during their growth spurts.
Feeding them puppy-specific food ensures they receive the necessary nutrients in manageable portions to support their development.
Choosing high-quality puppy food rich in proteins and healthy fats is crucial for their growth and overall health.

Switch to adult dog food when your puppy’s growth halts. This transition typically occurs at about 8 – 12 months for smaller breeds, around 12 months for medium breeds, and between 10 – 24 months for larger or giant breeds.
Select a well-balanced adult dog food to maintain their energy levels and avoid weight gain. Introduce the new diet gradually over a week to help their digestive system adjust and prevent stomach upsets.
How long until puppies reach full size?
Puppy growth varies widely, and predicting the exact time a puppy stops growing is challenging. However, their breed is often the most reliable indicator.
Breed specifics: Smaller breeds, like Dachshunds, reach adult size quicker compared to larger breeds such as Golden Retrievers or Labradors.
Sexual dimorphism: Another aspect is the puppy’s gender. Female dogs generally mature and grow to their full size quicker than males.
It’s crucial to monitor your growing puppy’s gear. Regularly checking their collar for a proper fit, ensuring you can slip two fingers between the collar and their neck, is essential.
When has a puppy reached its adult size?
A puppy is considered fully grown when they’ve reached maturity and their skeletal structure is fully developed. This varies from 8 to 24 months, depending on the breed.
If you’re uncertain about your puppy’s breed, especially in the case of a rescue or mixed breed, examining their paws can offer clues about their growth. Ideally, their paws should match their body size. Oversized paws may indicate more growth is expected.
However, paw size isn’t a foolproof indicator. Consulting a veterinarian for insights into your puppy’s possible lineage or age is advisable.
DNA tests can also be valuable in predicting your puppy’s adult size by identifying their breed composition, shedding light on another aspect of their story.
At what age do dogs reach their full size?
Breed Growth Timeline
The life cycle of a dog
There are four distinct stages in a dog’s life cycle: puppyhood, adolescence, adulthood, and the senior years.
Smaller breeds tend to mature and age faster than larger breeds, but lifespan can vary based on genetics, nutrition, and overall care.
Puppyhood
This stage is crucial for learning about life. Puppies should spend the first 8 weeks with their mother and littermates, gaining necessary love and nutrition.
During puppyhood, they learn social interaction with humans and other dogs, along with house and obedience training.
Vaccinations are vital in this stage to protect against diseases. It’s important to ensure they have received their initial vaccinations before going on their first walk.
Adolescence
This phase, marked by hormonal changes, typically starts between 6 – 18 months, varying with the breed. Adolescence often brings selective hearing and rebellious behaviors. Steady training is crucial for navigating this stage effectively.

Additionally, this is the time when dogs enter their first estrus or heat cycle, signaling sexual maturity.
During this period, behaviors such as increased urination, restlessness, or attraction from male dogs may be observed.
This is also the appropriate time to consider discussions about spaying or neutering with your vet, to manage breeding tendencies and health concerns related to reproductive activity.
Adulthood
A dog reaches full maturity in this stage. For smaller breeds, this might be around 18 months, while larger breeds can take up to 3 years.
Adult dogs have achieved emotional maturity and vigorous puppy energy stabilizes. The training and discipline from earlier stages pay off here, as adult dogs are usually well-behaved and house trained.
Senior years
This final stage is a dog’s ‘golden years’, typically starting around 7 – 10 years old, earlier for larger breeds. Senior dogs slow down, eat less, sleep more, and may start to show signs of aging like graying muzzles.
They might experience weakened senses and health issues such as joint or dental problems. Regular vet check-ups are essential during this time.
Top Tip: To determine your dog’s life stage and their equivalent human age, use a dog age calculator. It’s a fun way to understand their age in human years.
When does a dog reach adolescence?
The adolescent stage in dogs typically begins between 6 to 18 months, transitioning from puppyhood to adulthood.
This period is characterized by hormonal changes and mood swings, similar to the teenage phase in humans. The exact onset varies by breed and individual dog.
Duration of dog adolescence
The adolescence phase in dogs generally spans about a year, concluding around 18 to 24 months, depending on the breed.
Behavioral changes in adolescent dogs:
This life stage brings several common adolescent dog behavior challenges, but with consistent training and patience, they can be managed effectively.
Rebellion: Dogs often seem to forget their training as they become more curious and engage with their surroundings.
Challenges in recall are typical, as instinctual behaviors take precedence. Utilizing a long leash can provide freedom while maintaining control.
- Heightened Sniffing and Mounting: Hormonal shifts mean increased scent marking and mounting, particularly in males, though females might also exhibit these behaviors, especially during their heat cycle.
- Territorial Instincts: Dogs may show heightened protectiveness over objects or become more reactive to stimuli that previously didn’t bother them.
- Anxiety and Fearfulness: A second ‘fear period’ is common, where previously confident puppies may appear more cautious or scared. It’s vital to continue training to reinforce confidence, keeping routines predictable and calm, especially during the female’s heat cycle.
- Social Dynamics: Monitor your dog’s interactions with others as they might play more roughly, get easily distracted, or show less interest in socializing. If things escalate, redirect their attention to a game with you.
Adolescent dog training tips
Engaging in scent work is an excellent way to stimulate your dog mentally and physically. Hide treats or toys and encourage them to find them using their nose. This activity can be done indoors, in the garden, or during walks, providing the necessary exercise and mental stimulation for their age.
What marks the shift to adulthood in dogs?
After navigating through puppyhood and adolescence, you and your furry companion step into the adult dog phase.
Your once tiny, fluffy puppy is now fully grown, resembling a mature dog in appearance and, ideally, in behavior too. Yet, those endearing puppy eyes remain as charming as ever!
Caring for an adult dog, while generally easier than a puppy, still requires constant love and attention.
Ensuring regular exercise and proper diet is key to maintaining their health and happiness. Yearly veterinary visits and booster shots are also crucial to prevent various diseases.
Dogs, unfortunately, have a shorter lifespan compared to humans, and this varies significantly among breeds. Factors like genetics, living conditions, and size influence their longevity.
Typically, smaller breeds have longer lifespans, averaging from 7 to 14 years, while larger breeds may live between 5 to 13 years.
Remember, every dog is unique, and predicting their exact lifespan isn’t possible. Some dogs, under the right conditions, could live up to twenty years!
Focus on the signs of aging rather than the numbers. Older dogs might show less interest in physical activity and may have mobility issues.
Eventually, they’ll slow down, a reality all dog owners must face, though it’s not a pleasant thought.
Enhancing quality of life and longevity in dogs
After understanding the various stages of a dog’s life, from puppyhood to senior years, it’s important to consider how you can enhance their quality of life and potentially extend their lifespan.
- Regular Exercise and Diet: A balanced diet and consistent exercise routine are vital for maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being. This includes choosing the right type of food for their age, breed, and health condition.
- Yearly Veterinary Checks: Regular vet visits and keeping up with vaccinations and preventative care can catch health issues early and prevent serious diseases.
- Mental Stimulation: Engaging your dog’s mind through training, puzzle toys, and new experiences can help keep them sharp and prevent cognitive decline.
- Social Interaction: Regular interaction with other dogs and people can help maintain their social skills and overall happiness.
- Proper Grooming: Regular grooming, including brushing their coat, trimming nails, and dental care, is essential for their hygiene and comfort.
- Comfortable Living Environment: Ensure your dog has a comfortable, safe space in your home, with a cozy bed and access to their favorite toys.
- Using Collars and Harnesses Appropriately: Properly fitting collars and harnesses are essential for safe walks and preventing injuries. A well-fitting harness can distribute pressure more evenly than a collar, which is especially important for dogs prone to respiratory issues or neck strain.
- Monitoring Health Changes: Be vigilant about any changes in your dog’s behavior or physical condition, as these can be early signs of health issues.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity can lead to numerous health problems. Keeping your dog at a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial.
- Emotional Support and Affection: Never underestimate the power of love and affection. Spending quality time with your dog, petting, and playing can greatly enhance their quality of life.
- Stress Reduction: Dogs can be sensitive to stress. Keeping their environment calm and predictable can contribute to a happier, healthier life.

Conclusion
As you journey through the different stages of your dog’s life, from the playful puppy days to the serene senior years, it becomes clear that the question “when is a dog considered an adult” encompasses more than just physical growth.
It’s a blend of physical development, emotional maturity, and behavioral changes. Typically, this transition to adulthood occurs between 1 and 2 years of age, but it varies with breed size and individual differences.
Remember, reaching adulthood doesn’t just signify the end of growth; it also marks the beginning of a phase where your consistent care, training, and companionship mold your pet’s personality and health.
By providing a balanced diet, regular exercise, proper medical care, and emotional support, you not only enhance their quality of life but also cherish and extend these precious years with your faithful companion.

